Measuring Wealth
Hi, The Investor’s Podcast Network Community!
Welcome back to We Study Markets!
Fun fact: On this day in 1927, Charles Lindbergh made the first solo nonstop transatlantic flight, traveling from New York to Paris in about 33 hours 🛩️
As someone who doesn’t love flying, I’m very thankful that travel time has been cut down.
Today, we’ll discuss what conventional measures of wealth fail to capture, and more, in just 4 minutes to read.
— Shawn
Get smarter about valuing businesses in just a few minutes each week.
Get the weekly email that makes understanding intrinsic value
easy and enjoyable, for free.
QUOTE OF THE DAY

“The problem with gross domestic product is the gross bit. There are no deductions involved: all economic activity is accounted as if it were of positive value. Social harm is added to, not subtracted from, social good.”
Trade economic and financial events on Kalshi, the first regulated exchange to trade what inflation or fed rates will be, whether the debt ceiling will be raised, or if TikTok will be banned.
With hundreds of event contracts and traditional assets like S&P and FX, you can hedge your portfolio against specific risks or profit from accurate predictions on global trends.
WHAT ELSE WE’RE INTO
📺 WATCH: Intrinsic value analysis of Copart, a long-term compounder
👂 LISTEN: Why the financial crisis isn’t over yet, with Jeff Snyder
📖 READ: The P/E ratio, what it is, and how to use it
GDP IS OVERRATED
Defining wealth
Over 200 years ago, the Scottish politician and writer, James Maitland, wrote that wealth “consist(s) of all that man desires, as useful and delightful to him.”
In context, he meant that a nation’s wealth is not just the sum of individual households’ and businesses’ riches.
In the centuries since, we’ve made tremendous progress using machines and technology to boost output (the total quantity of things produced). The productivity gains have hugely alleviated poverty, enabling more and more people to enjoy what they find “useful and delightful.”
Defining and measuring wealth is a topic David Stein, host of the Money for the Rest of Us podcast, explored recently, inspiring most of what we outline today.

Slowly, then suddenly
The economist, Angus Maddison, has also explored this topic, outlining how gross domestic product (GDP) per capita has evolved. He found that (using 2011 dollars) per capita GDP in the year 1 AD was $747.
Flash forward 1,000 years, and that figure had fallen to $723. By the 16th century, it was around $900, and by the year 1800, it was only $1,100 — not even double what those during the Biblical era would’ve experienced.
This changed dramatically during the Industrial Revolution. Between 1820 and 1900, per capita GDP worldwide doubled.
By 1950, it was $3,300. As of 2016, it was $14,600. And those are global figures, the rate of wealth acceleration, as measured by GDP, has been far more dramatic in developed countries.
Living longer
Life expectancy followed a similar trajectory: Two millennia ago, the average life expectancy was just 24 years old — brought down by child mortality rates. By 1900, it was only 31 years and only 46 years in 1950.
However, by 2000, the average life expectancy globally was 66 years, climbing to 73 for nearly 8 billion people in 2020.
Better sanitation, and access to healthcare, including vaccinations and improved medical treatments, contributed meaningfully to this sudden improvement in life expectancy.
In this case, more output/GDP correlates strongly with better living conditions and greater wealth, allowing more people to enjoy what they find “useful and delightful,” as Maitland would say.
Yet, higher GDP levels don’t perfectly correlate to this definition of wealth. As Stein explains, today, life expectancy in Portugal is 81 years, higher than in the U.S. at 77 years. Even Costa Rica, at 79 years, boasts a higher life expectancy than the U.S.
But Americans have by far the highest per capita GDP of this group at $70,200, compared to only $12,500 in Costa Rica and $24,500 in Portugal.
GDP isn’t everything
What’s the point of being “wealthier” if you don’t live as long to indulge in what you find useful and delightful? Clearly, there are shortcomings in our modern measurements of wealth and living standards, namely GDP.
Stein suggests that we can get higher life expectancies and education levels at lower levels of per capita GDP than in the U.S.
In 1930, the well-known economist John Maynard Keynes speculated about the future that his grandchildren would enjoy.
He projected that by 2030 living standards would be between four and eight times greater. And he was right; global per capita GDP is about four times higher today.
Still, his conclusions were off: Keynes thought most people would work just 15 hours per week. He imagined that there would be so much abundance that many would lose interest in working as much.
Evidently, this part hasn’t come to fruition despite the increases in material abundance as reflected by GDP.
On that same point, the U.S. has seen considerable relative increases in economic output versus other major G7 economies, including countries like Japan, Germany, and the UK. In 1990, the U.S. accounted for 40% of the G7’s economic output.
More recently, that figure has jumped to 58%.
Three decades ago, per capita GDP in the U.S. was 24% higher than in Western Europe, but now it’s 30% higher.
Cultural trade-offs
America has mastered the art of GDP. As a country, it’s excellent at boosting this measure of wealth. GDP, though, hardly captures true living standards — does anyone really believe that Americans are 30% happier/better off than their Western European peers? Probably not.
The U.S. is an extremely advanced, productive economy. That results in more aggregate income, boosting earnings widely. Hence, a truck driver in Oklahoma can earn more than a doctor in Portugal, as Stein explains.
Clearly, money, or more specifically, GDP, isn’t everything. As some would say, Europeans seemingly make a trade-off between quality of living and income.
Instead of clogged highways and consuming work lives (generalizing here), they prefer walkable cities, longer holidays and maternity leave, and more accessible public health care.

Could the differences in living quality after a certain threshold of per capita GDP be simply cultural?
Said differently, are Europeans embodying Keynes’ vision of working less and cherishing the riches born out of economic advances more than Americans?
Maybe, but Stein thinks that’s not the full picture.
He emphasizes that, as outlined in The Economist, Americans are getting richer (on a GDP basis) because American workers are getting more productive, more quickly, than workers in other developed economies.
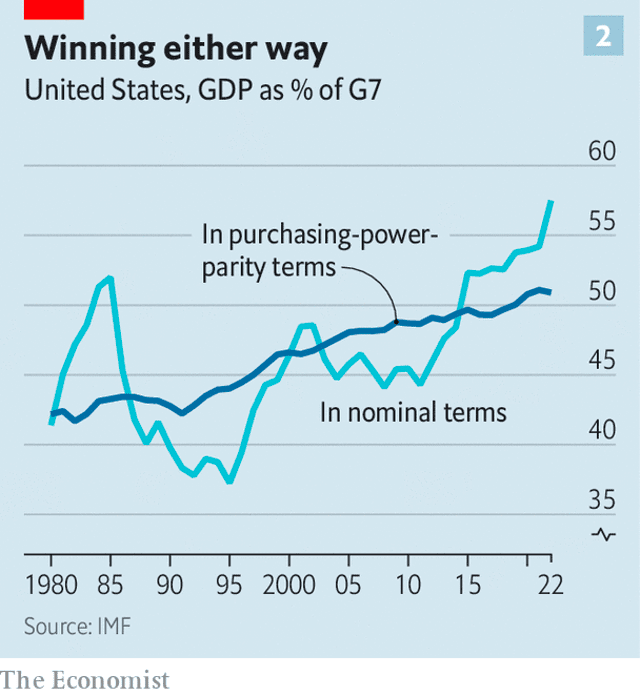
Quoting the economist, “The Conference Board, a think-tank…has found that between 1990 and 2022, American labor productivity (what workers produce in an hour) increased by 67%, compared with 55% in Europe and 51% in Japan.”
America, as a whole, is getting a bigger slice of a growing pie, but that GDP wealth isn’t necessarily being used to optimize for other forms of wealth, such as well-being and life expectancy.
Dive deeper
For more, listen to David Stein’s podcast episode “How Should Personal and National Wealth be Measured?”
And be sure to sign up for his excellent weekly newsletter here — it’s one of our favorites.
SEE YOU NEXT TIME!
That’s it for today on We Study Markets!
Enjoy reading this newsletter? Forward it to a friend.